回覆 4# 抽刀斷水
which social structure of human can't be explained by evolution?
It's important to understand that the application of evolutionary principles to complex human social structures is a very nuanced and often debated area. While evolutionary biology can offer insights into the origins of certain social behaviors, it doesn't fully explain the intricate details of how societies are structured today. Many factors beyond purely biological evolution play a crucial role, including culture, history, technology, and individual choice.
That being said, some aspects of human social structure are harder to fully explain through a purely evolutionary lens, particularly when those aspects seem to contradict what might be expected from simple natural selection:
Large-scale cooperation among unrelated individuals: While kin selection (favoring relatives) and reciprocal altruism (expecting payback) explain some cooperation, humans often cooperate in very large groups with people they are not related to and may never interact with again. Explaining the evolution of this level of cooperation is complex and involves factors like cultural evolution, group selection (a controversial idea), and reputation.
Highly variable mating systems: Humans exhibit a wide range of mating systems, from monogamy to polygyny to polyandry, and these can vary significantly across cultures. While evolutionary explanations exist for some mating preferences, the sheer diversity and fluidity of human mating systems are not easily reduced to simple biological imperatives.
Complex social hierarchies: While dominance hierarchies exist in some animal species, human social hierarchies are far more complex and involve factors like wealth, power, status, and ideology. Evolutionary psychology can offer some insights into the psychological underpinnings of status-seeking behavior, but it doesn't fully explain the specific forms that social hierarchies take in different societies.
Rapid cultural evolution: Human cultures evolve much faster than biological evolution. Technological advancements, social norms, and belief systems can change dramatically within a few generations, far outpacing the pace of genetic change. This rapid cultural evolution can lead to social structures that are not easily explained by slow biological evolution.
Altruism towards strangers: While some altruism can be explained by kin selection or reciprocity, humans sometimes show altruism towards complete strangers, even at a cost to themselves. Explaining this type of behavior is challenging from a purely evolutionary perspective and may involve factors like empathy, moral reasoning, and cultural norms.
It's crucial to avoid what's called the "naturalistic fallacy" – the idea that what is natural is necessarily good or justifiable. Just because a behavior might have an evolutionary basis doesn't mean it's morally right or that we should necessarily perpetuate it. Human societies are shaped by a complex interplay of biology, culture, and individual agency, and we have the capacity to make choices that go beyond our evolutionary predispositions.
In conclusion, while evolutionary principles can provide valuable insights into the origins of some human social behaviors, they don't fully explain the complexity and diversity of human social structures. Many other factors, including culture, history, technology, and individual choice, play a crucial role in shaping how societies are organized.
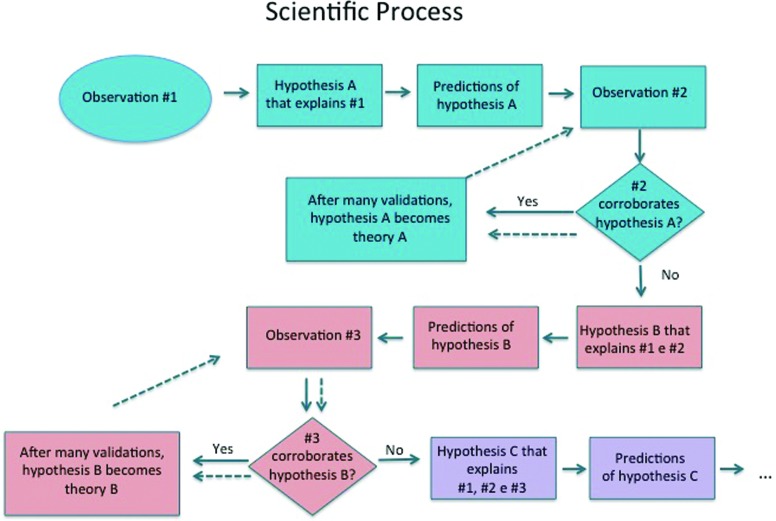
咁點corroborates the hypothesis呢?
scientific process, 觀察到有不符理論嘅現象,咪好大機會個理論係錯囉。咁演化論又有咩嘗試過解釋到上面嘅現象吖?
Darwinism 同 neo Darwinism都係以natural selection為基礎,Natural selection點解釋到上面嘅行為? |









 遊客 2025/2/18 11:43
|
遊客 2025/2/18 11:43
| 



 2025/2/20 16:13
|
2025/2/20 16:13
| 
